'It’s possible to end AIDS in Tijuana, but we need to take a broader look,' says UC San Diego's Steffanie Strathdee. The trials she and fellow researchers faced in northern Mexico are recounted in UCTV's new four-part documentary.
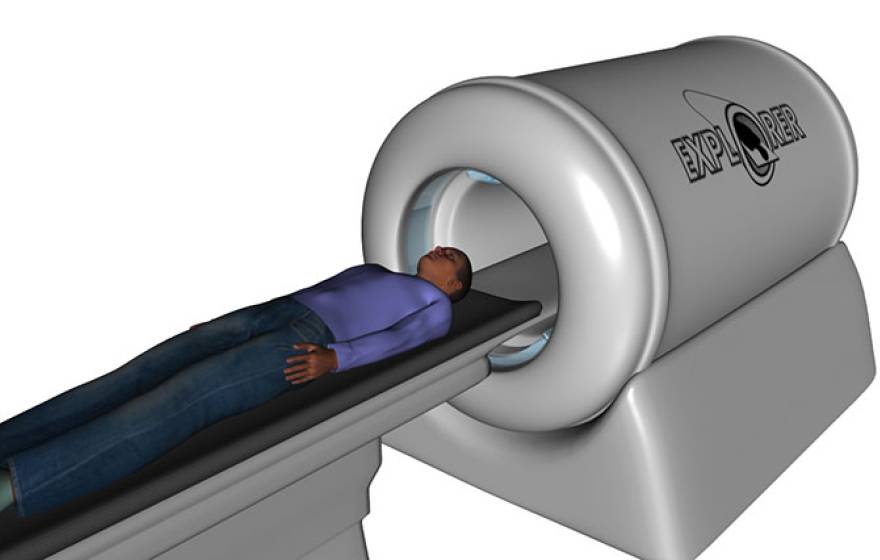
Researchers awarded $15.5M to build first total-body PET scanner
New technology could fundamentally change the way cancers are tracked and treated.
Patient, test thyself
Wireless mobile devices have been developed to monitor everything from eating to stress levels.
$9.75M will launch platform to accelerate mobile health research
Success of the Health eHeart Study was the impetus for the creation of the Health ePeople project.
High tech health gives hope to sick and injured
San Diego County has become a hotbed of medical innovation, led by UC San Diego and other institutions.
High-fructose diet hampers recovery from traumatic brain injury
A sweet may sound like a treat, but a steady diet of them also may impair recovery from mental deficits after head trauma.
UCLA and VA launch program to enhance cancer care for veterans
UCLA-VA pilot project is nation’s first to offer veterans access to cutting-edge cancer clinical trials and state-of-the-art treatment facilities.
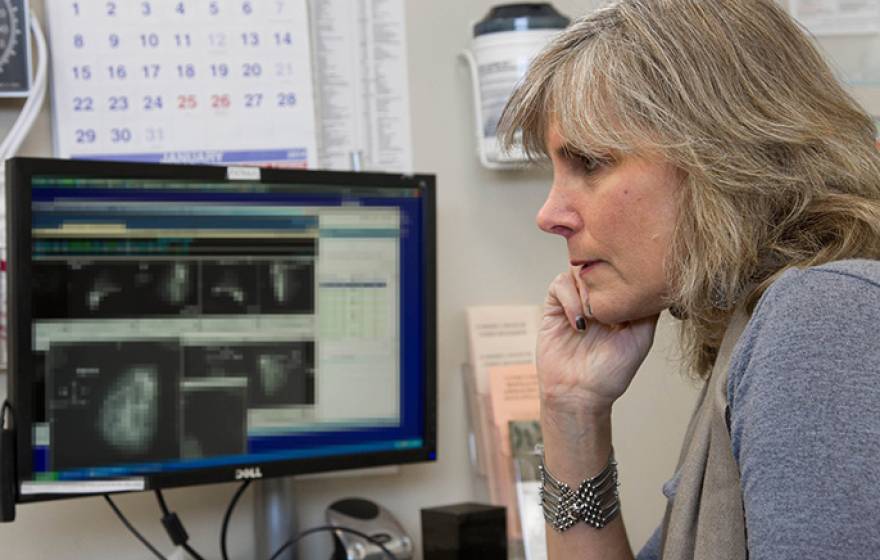
Five things women should know about breast cancer
UC San Francisco's Dr. Laura Esserman, who leads the Athena Breast Health Network — a collaboration of the five UC medical centers — offers insights into breast cancer.
Investigating link between thirdhand smoke and cancer
Berkeley Lab gets $1.3M to study health impacts of the stubborn, noxious residue left behind from smoked tobacco.
Chip-based technology enables reliable direct detection of Ebola virus
System can be integrated into simple, portable instrument for use in field situations where rapid, accurate detection of the virus is needed to control outbreaks.
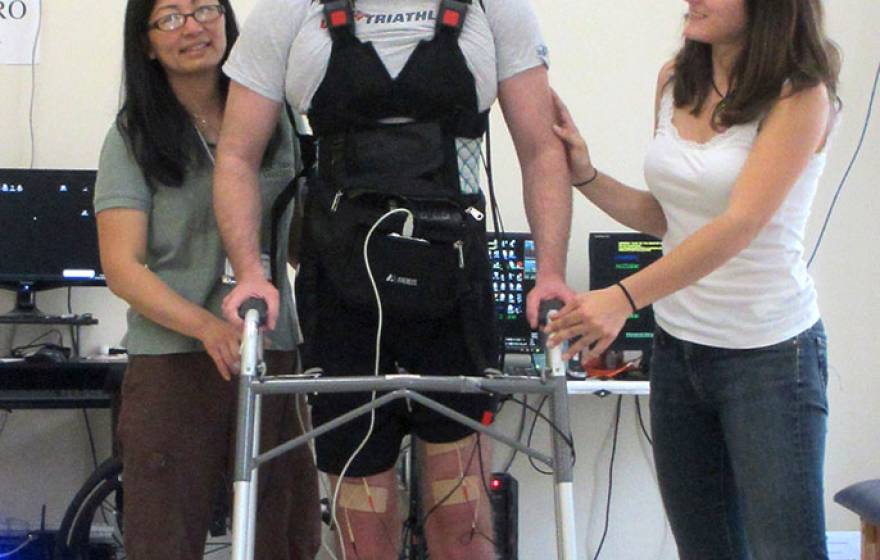
Paralyzed man walks with help of brain-computer interface
Mind-controlled technology bypasses spine and creates gateway to a host of medical possibilities.
UCSF Fresno marks 40 years of serving Central Valley
The campus is established as the largest provider of graduate medical education in the valley, where the population has grown faster than the number of doctors available.