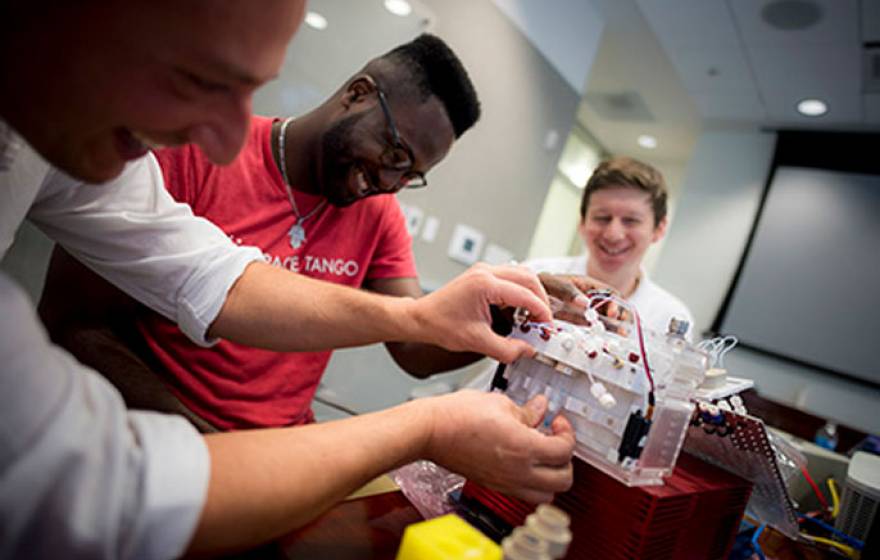
For the University of California, summer is a time to be unusually experimental, adventurous and productive.
How UC spends the summer months
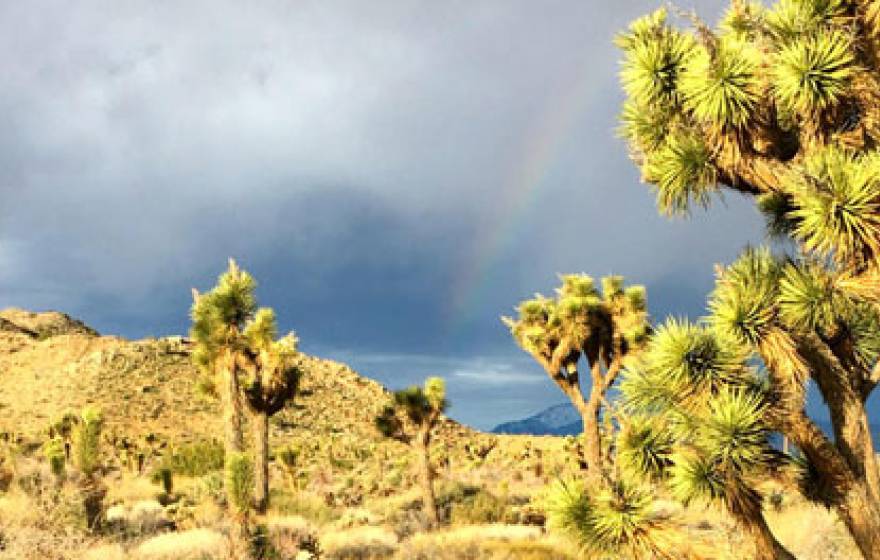
Iconic Joshua trees are facing extinction
The national park would retain just 0.02 percent of its tree habitat if no climate change action is taken.
New robotic lens lets you zoom in by blinking your eye
The lens is the first example of an interface between humans and soft machines. Is ‘The Terminator’ next?
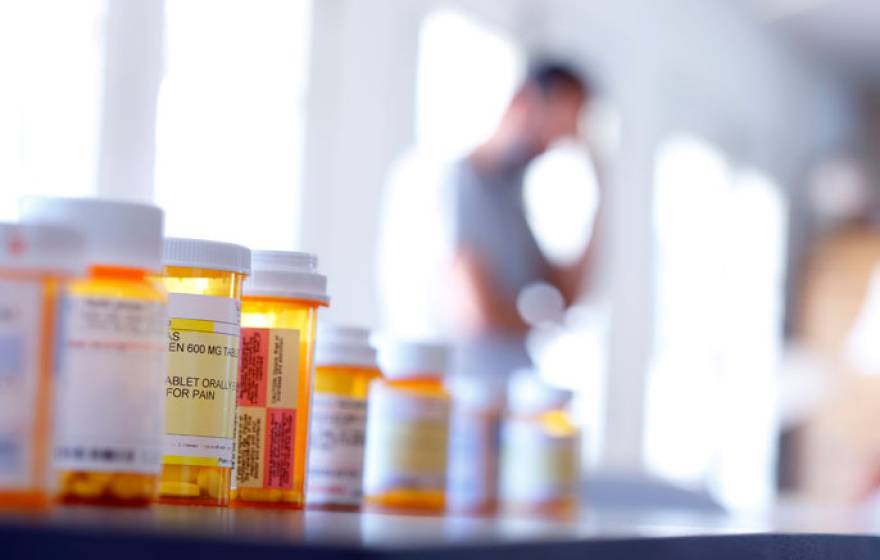
Finding non-opioid alternatives for cancer pain
Doctors are investigating a variety of new treatments to end cancer patients’ pain and give them hope.
Spotting misinformation online via artificial intelligence
Computer scientist William Wang’s deep learning project aims to understand the spread of online misinformation.
Like to wake up really, really early? You're not quite one in a million — but you are 1 in 300
A genetic trait may be behind those who thrive on very-early-to-bed, very-early-to-rise lifestyles.
How cilantro works as a secret weapon against seizures
Cilantro has been used as food and medicine for 8,000 years. Now, scientists know how it works to curb epileptic seizures.
UC Davis and USAID launch new research program to study rural poverty worldwide
The effort aims to find solutions to root causes of poverty and food insecurity.
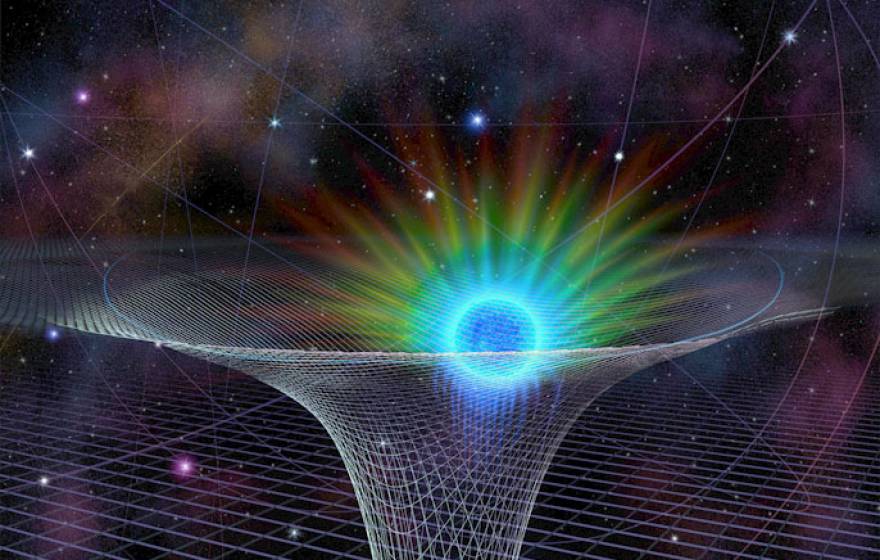
Einstein was right about relativity, UCLA says — for now
Welcome to ‘extreme astrophysics’ — the most detailed study ever of a supermassive black hole and Einstein’s general theory of relativity.
Alzheimer's gene may impact cognition before adulthood
A new finding suggests a gene linked to Alzheimer's may also be associated with lower IQ scores in childhood.
The case against reality
Evolution has trained humans to construct reality, rather than to see the world as it truly is.
Why are humans the only species prone to heart attacks?
Gene loss 2 to 3 million years ago may explain why coronary events are common in humans but rare in other animals.