Newly identified chemical compound restores transparency to mouse lenses and human lens tissue.
UC San Francisco |
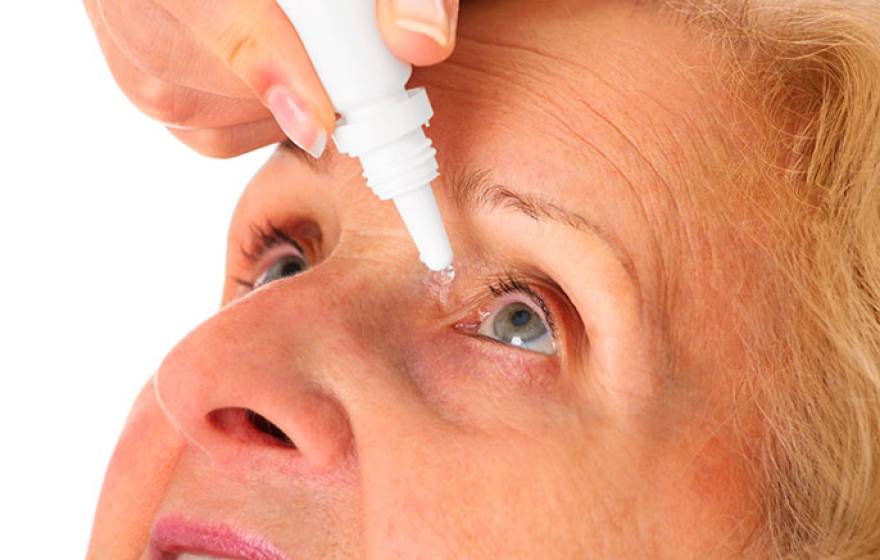
Clearing cataracts with eye drops
UC San Francisco |
Bike injuries rise, especially among older riders
Resurgence of cycling is taking a toll on middle-aged cyclists: More are getting hurt, and their injuries are more serious.
UCLA |
More than 750,000 elderly Californians ‘unofficially’ poor
1 in 5 older adults have incomes above the federal poverty level, but still struggle to pay their expenses.
UCLA |
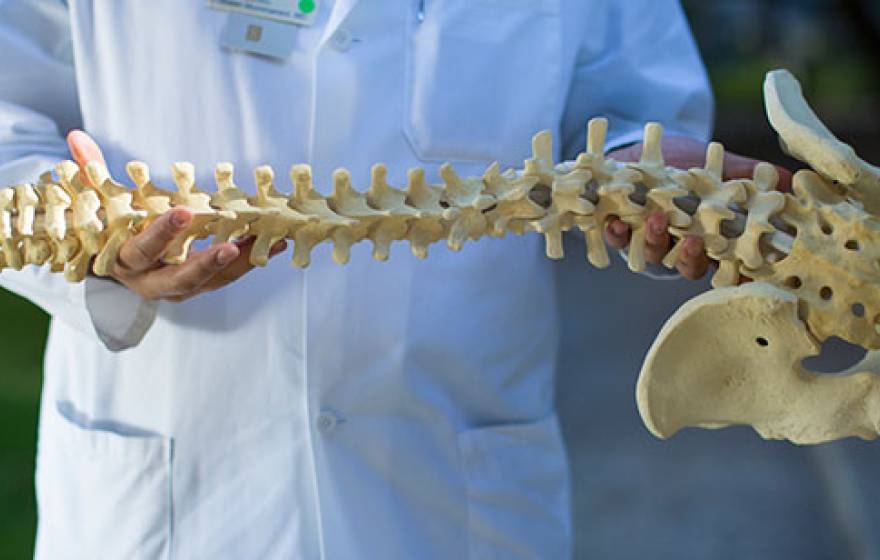
Bone-building protein stimulates bone stem cells
Study results could mean good news for people with osteoporosis or those with traumatic bone injuries.
UC San Francisco |
Longevity hormone is lower in stressed and depressed women
The hormone klotho, which regulates aging and enhances cognition, offers possible new link between mind and body.
UC Berkeley |
Drug perks up old muscles and aging brains
Drug perks up old stem cells in both brains and muscles of mice, pointing the way to drug interventions for humans that would make aging tissues throughout the body act young again.
UCLA |
The stranger within: Connecting with our future selves
Social psychologist studies the emotional disconnect between who we are now, and who we will be years from now.
UC Newsroom |
Healthy elders may hold key to fighting cancer
'Wellderly' may have unknowingly fought — and beaten — cancer; their immune systems may hint at how.
UCLA |
Meditation may slow age-related loss of gray matter in the brain
A new study by UCLA researchers found that meditation appeared to help preserve the brain’s gray matter, the tissue that contains neurons.
UC Newsroom |
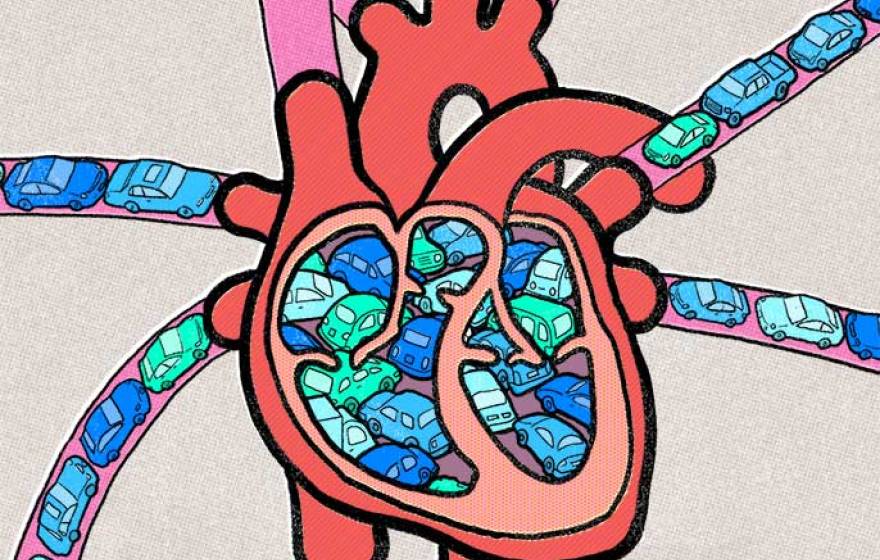
How traffic jams affect heart health
Clogged interstates aggravate clogged arteries, according to research by a UC Irvine graduate student.
UC San Francisco |
Sugary soda linked to cell aging
Scientists find shorter telomeres — the protective units of DNA that cap the ends of chromosomes — in immune cells of soda drinkers.
UCLA |
Biologists delay the aging process by ‘remote control’
Researchers have identified a gene that can slow the aging process throughout the entire body when switched on in key organ systems.